As cyber threats continue to rise, organizations can no longer afford to treat security as an afterthought. This is where SSDLC, or Secure Software Development Lifecycle, comes into play. SSDLC is a structured approach that embeds security controls, testing, and best practices into every phase of software development, helping teams prevent vulnerabilities before they reach production.
This guide explains what SSDLC is, how it works, its phases, benefits, and how it differs from traditional SDLC.
What Does SSDLC Stand For?
SSDLC stands for Secure Software Development Lifecycle. It is an enhanced version of the traditional Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC) that prioritizes security from planning through maintenance.
Rather than fixing security flaws after deployment, SSDLC focuses on early detection, risk reduction, and continuous protection.
Why SSDLC Is Important
Modern applications handle sensitive user data, financial information, and critical infrastructure. Without SSDLC, security flaws often surface too late—when they are expensive and dangerous to fix.
Key Benefits of SSDLC
- Reduces security vulnerabilities early
- Lowers breach remediation costs
- Improves regulatory compliance
- Enhances user trust and brand reputation
- Minimizes downtime and incident response efforts
SSDLC Phases Explained
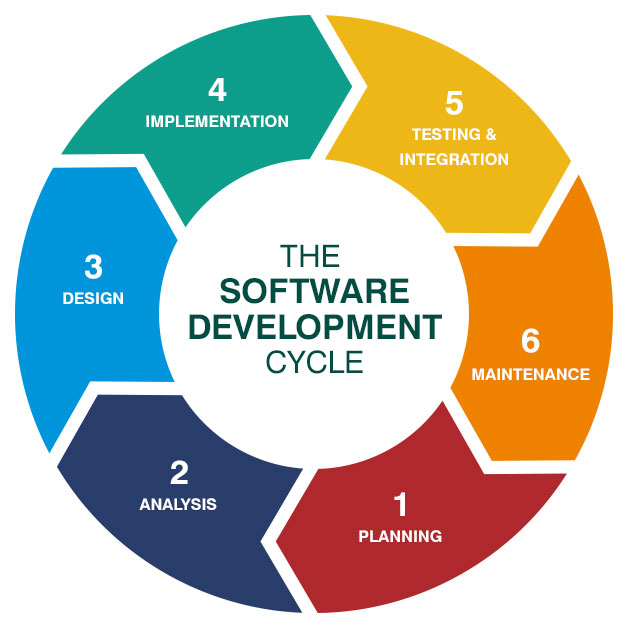


1. Planning & Requirements
Security begins at the planning stage by identifying risks and defining protection goals.
- Define security and compliance requirements
- Perform risk assessments
- Identify sensitive data and access controls
2. Secure Design
In this phase, architects design systems to withstand attacks.
- Threat modeling (e.g., STRIDE)
- Secure architecture design
- Least privilege and defense-in-depth principles
3. Secure Development (Implementation)
Developers write code following secure standards.
- Secure coding guidelines
- Approved libraries and frameworks
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
4. Security Testing & Verification
Testing ensures vulnerabilities are detected before release.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
- Penetration testing
- Dependency vulnerability scanning
- Manual code reviews
5. Secure Deployment
Security controls are validated before production launch.
- Secure configuration and hardening
- Secrets and credential management
- Infrastructure and cloud security checks
6. Maintenance & Monitoring
Security continues after deployment.
- Continuous monitoring and logging
- Patch and vulnerability management
- Incident response and remediation
SSDLC vs Traditional SDLC
| Feature | SDLC | SSDLC |
|---|---|---|
| Security timing | Late or optional | Built-in from start |
| Risk management | Reactive | Proactive |
| Cost of fixes | High post-release | Lower early-stage |
| Compliance readiness | Limited | Strong |
SSDLC vs DevSecOps
While SSDLC defines what security activities should happen, DevSecOps focuses on how to automate and integrate them into CI/CD pipelines. Many modern teams use SSDLC as the foundation and DevSecOps for execution.
Common SSDLC Frameworks
Organizations often align SSDLC with established standards, including:
- Microsoft Secure Development Lifecycle (SDL)
- NIST Secure Software Development Framework (SSDF)
- OWASP Software Assurance Maturity Model (SAMM)
Who Should Use SSDLC?
SSDLC is essential for:
- SaaS platforms
- Financial and healthcare applications
- Government and enterprise software
- Any application handling user data or payments
Final Thoughts
The Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. By integrating security into every phase of development, organizations can reduce risk, save costs, and deliver safer software at scale.
If security matters to your users, SSDLC should be part of your development strategy.

